Summary
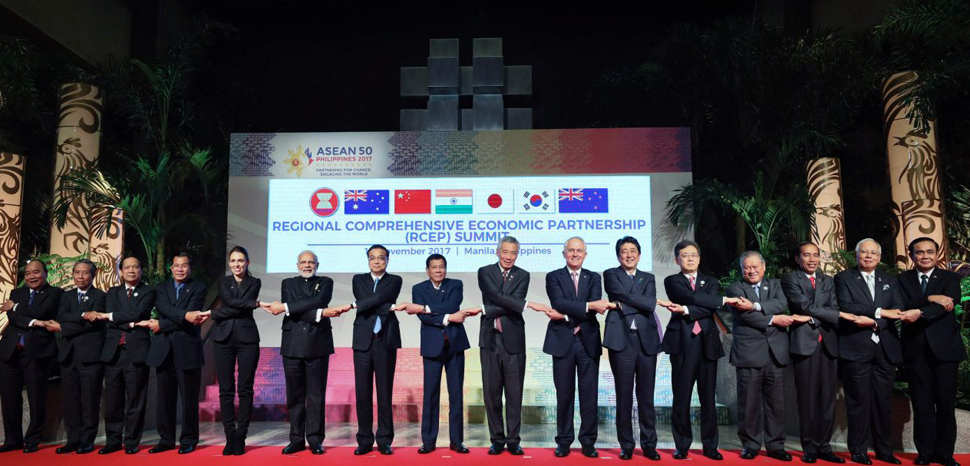
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), signed in November 2020 by fifteen countries of the Asia-Pacific region, represents one of the world’s largest free trade agreements (FTA). The scope of the RCEP is vast; the agreement seeks to liberalize trade between the emerging markets of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and advanced economies like China, South Korea, and Japan – three countries that will undergo this kind of economic integration for the first time. As always happens in such cases, the effects of the RCEP will not be immediate and will not be equally distributed among members; but the reduction of tariffs and, most importantly, non-tariff barriers will spur economic growth in the medium-long term. And one country will be conspicuously absent from the region’s economic fortunes: the United States.
Background
What is the RCEP?
The RCEP is a large-scale FTA between fifteen countries of the Asia-Pacific region. Its membership consists of the 10 ASEAN countries (Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Myanmar, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Singapore and Indonesia) plus China, South Korea, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand. The project was first proposed in 2011 by ASEAN, with the first round of negotiations taking place two years later. The deal encompasses about 30% of the world’s population and GDP as well as more than 27% of global trade; in contrast to the 15% represented by the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), another FTA between eleven countries across the Pacific that entered into force in 2018 (sans the United States). The RCEP brings together an eclectic mix of economies; it represents the first trade liberalization deal between China, Japan, and South Korea – three of the largest and most advanced economies on the planet – and it also includes emerging economies like Vietnam or Indonesia, along with a global business hub in Singapore.